Windows Server 2012 R2 Capability : Server virtualization
When you optimize your business for the cloud with Windows Server 2012 R2, you take advantage of your existing skillsets and technology investments. You also gain all the Microsoft experience behind building and operating private and public clouds – right in the box.
Delivered as an enterprise-class, the simple and cost-effective server and cloud platform Windows Server 2012 R2 delivers significant value around seven key capabilities:
Server Virtualization
Windows Server Hyper-V offers a scalable and feature-rich virtualization platform that helps organizations of all sizes realize considerable cost savings and operational efficiencies. With Windows Server 2012 R2, server virtualization with Hyper-V pulls ahead of the competition by offering industry-leading size and scale that makes it the platform of choice for running your mission critical workloads. Using Windows Server 2012 R2, you can take advantage of new hardware technology, while still utilizing the servers you already have. This functionality enables you to virtualize today and be ready for the future tomorrow.
Whether you are looking to expand virtual machine mobility, increase virtual machine availability, handle multi-tenant environments, gain bigger scale, or gain more flexibility, Windows Server 2012 R2 with Hyper-V gives you the platform and tools you need to increase business agility with confidence. Plus, you can also benefit from workload portability as you extend your on-premises datacenter into a service provider cloud or Windows Azure.
Enterprise-class scale and performance
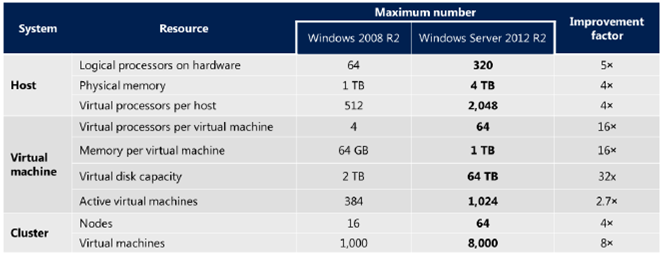
Windows Server 2012 R2 offers massive scale to help transform your datacenter into an elastic, always-on cloud. For example, Hyper-V in Windows Server 2012 R2 provides industry-leading virtualization host support for 320 logical processors, 4TB of physical memory, and 1,024 active virtual machines per host. Hyper-V also supports 64-node clusters and 8,000 virtual machines per cluster as well as a 64 TB virtual disk format with the ability for online resize – the ability to grow or shrink a VHDX-formatted virtual disk dynamically while it is running, without downtime.
Live migration is an important virtual machine mobility feature that has continued to improve since it was introduced with Windows Server 2008 R2. In Windows Server 2012 R2, these performance improvements have been taken to the next level. Live migration compression accelerates live migration transfer speed by compressing the VHD/VHDX file, improving performance by roughly 2x for most workloads. Live migration with remote direct memory access (RDMA), another new feature in Windows Server 2012 R2, delivers the highest performance for live migrations over >10 GB network connections, supporting transfer speeds of up to 56 Gigabytes, by offloading the transfer to hardware and harnessing the power of RDMA technologies.
Virtualized Microsoft workloads, such as Exchange, SQL, and SharePoint, run best on a Hyper-V infrastructure. For example, independent third-party testing by The Enterprise Strategy Group, Inc. (ESG Lab) showed that an Exchange Server 2013 infrastructure deployed within twelve Hyper-V virtual machines running on a single physical server supported the I/O requirements of up to 48,000 simulated users. The average database read-response times ranged between 5.02 and 15.31 milliseconds, well below the Microsoft recommended limit of 20 milliseconds. In another ESG Lab test case, an existing SQL Server 2012 online transaction processing (OLTP) workload, virtual processor (vCPU)-limited by the maximum allowed configuration of four vCPUs imposed by Windows Server 2008, increased performance by six times by taking advantage of 64 vCPUs in Windows Server 2012. The average transaction response times also improved five times, from four vCPUs to 64 vCPUs.
Windows Server 2012 R2 also introduces generation 2 virtual machines to Hyper-V. These virtual machines provide Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI )firmware support, Pre-Boot Execution Environment (PXE) boot, secure boot, and boot from a Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) virtual hard disk VHD. Some older virtual hardware such as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) controllers has been removed. This change can help contribute to faster boot times and more flexible configurations. However, Windows Server 2012 R2 only supports more recent operating systems and does not support conversion between generation 1 and generation 2.
These enterprise-class features help ensure that your virtualization infrastructure can support the configuration of large, high-performance virtual machines for sustaining Microsoft or other, mission-critical workloads that you might need to significantly scale.
Virtual machine mobility
Windows Server 2012 R2 enables you to manage virtual machines independently of their underlying physical infrastructure. In addition, Windows Server 2012 R2 also enables you to handle changes in resource demand as they occur and gives you the ability to rebalance running virtual machines either through the servers on which the virtual machines reside or the storage resources used by the virtual machines.
Introduced with Windows Server 2012 as an industry-first capability, shared-nothing live migration enables you to move a virtual machine, live without downtime, from one physical system to another, even if the systems are in different clusters or not connected to the same shared storage. This capability means you can live-migrate a virtual machine from one cluster to a different cluster without setting up complex storage mappings. Such functionality can prove beneficial in many different situations, such as in a branch office where you may be storing the virtual machines on a local disk, and you want to move a virtual machine from one node to another. This feature also can prove useful when you have two independent clusters and you want to move a virtual machine, live, between them, without having to expose their shared storage to one another. Windows Server 2012 R2 also introduces cross-version live migration that enables you to move virtual machines from a server or cluster running Windows Server 2012 to a server or cluster running Windows Server 2012 R2 with no downtime. In multi-tenant environments of service providers, tenants are frequently asking for application-level, high availability for their workloads. To address this need, Windows Server 2012 R2 provides complete flexibility with multiple options for guest clustering, without making you sacrifice agility and density in your environment. In addition to Fibre Channel, iSCSI, and server message block (SMB) protocol support, Windows Server 2012 R2 now also offers shared VHDX files. Shared VHDX files can be stored either on a scale-out file server cluster or on cluster-shared volumes (CSV) on block storage. Shared VHDX clustering also preserves dynamic memory, live migration, and storage live migration for a virtual machine that is part of the guest cluster.
First introduced in Windows Server 2012, Hyper-V Replica provides a storage- and workload-agnostic solution that replicates efficiently, periodically, and asynchronously over IP-based networks, typically to a remote site. Hyper-V Replica also enables an administrator to easily test the replica virtual machine without disrupting the ongoing replication. If a disaster occurs at the primary site, administrators can quickly restore their business operations by bringing up the replicated virtual machine at the replica site. New in Windows Server 2012 R2, Hyper-V Replica enables configurable, replication frequencies down to 30 seconds or up to 15 minutes. Furthermore, Hyper-V Replica now supports multiple nodes, meaning tertiary replica sites for example, such as in the case of a service provider who wants to replicate a customer’s workload to another datacenter.
Another innovation around Windows Server 2012 R2 is Windows Azure Hyper-V Recovery Manager. Hyper-V Recovery Manager combines Windows Azure, System Center Virtual Machine Manager, and Hyper-V Replica to deliver planned and cost-effective business continuity of workloads. With Windows Azure Hyper-V Recovery Manager, you can protect services by automating the replication of the virtual machines that composes them at a secondary location. Hyper-V Recovery Manager also provides continuous health monitoring of the primary site and coordinates the orderly recovery of services in the event of a site outage.
First-class citizen support for Linux as a guest
Many enterprise IT departments and service providers today run a mix of hypervisors, operating systems, and applications in their datacenter. Oftentimes, migrating from one platform to another is not possible or even feasible from a technical standpoint due to the size and scope involved. Designed to integrate well with heterogeneous IT environments, Windows Server 2012 R2 supports a cross-platform cloud infrastructure by adding comprehensive functional support for Linux guests running on top of Hyper-V.
Dynamic Memory, a Hyper-V feature first introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, automatically reallocates memory between virtual Cloud optimize your business with Windows Server 2012 R2 9
machines running on a Hyper-V host. This results in a more efficient allocation of virtual machine memory while dramatically increasing virtual machine consolidation ratios. In Windows Server 2012 R2, Hyper-V now offers full dynamic memory support for Linux guests including:
Minimum memory setting — ability to set a minimum value for the memory assigned to a virtual machine lower than the startup memory setting.
Hyper-V smart paging — paging used to enable a virtual machine to reboot while the Hyper-V host is under extreme memory pressure.
Memory ballooning — reclaiming unused memory from a virtual machine for another virtual machine with memory needs.
Runtime configuration — adjusting the minimum memory and maximum memory configuration setting on the fly, without requiring a reboot, while the virtual machine continues to run.
Also, previously, if you wanted to take advantage of Linux Integration Services (LIS) for your Hyper-V environment, you had to go to the Microsoft Download Center, download the correct LIS package for your Linux distribution, and then manually install it on your Hyper-V servers. With Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V hosts, key Linux vendors have included LIS for Hyper-V in their standard distributions, eliminating the manual step required to take advantage of the latest LIS capabilities.
Reference by: https://www.microsoft.com
